What is Big Data?
Big data

Source: https://stories.freepik.com/illustration/server/pana
Introducing Big Data
Let’s start with understanding what Big Data is. Big Data is the combination of massive amounts of data collected, stored and analyzed by organizations. This data can be mined for information to be used in machine learning projects and advanced analytics to provide a new and effective way for data management decision support.[1]
In other words, Big data is the information companies and organizations collect from the data constantly generated anytime we open an app, search on Google or simply travel place to place with our mobile devices. Sounds easy right? But how to make use of this data?
The 5Vs
If you want to make an effective use of this revolutionary amount of data, it is essential that you understand the various features of Big Data first.
Traditionally, Big Data has been defined and based on three dimensions: Volume, Variety and Velocity. Yet, two dimensions have been recently added in order to enable users to create knowledge through Big Data, these are Veracity and Value. Too many Vs? Let’s see them one by one!
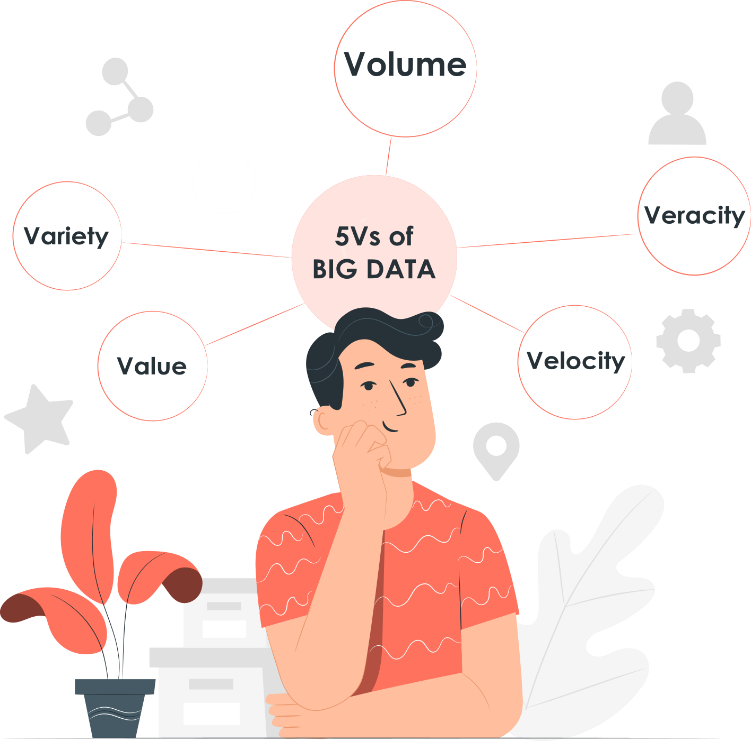
Source: Edited from stories.freepik.com
- Volume: let’s begin with the Volume, it refers to the size of data sets that need to be analyzed and processed. These data sets are frequently larger than terabytes and petabytes. Data can be considered as Big Data or not, based on its volume.
- Velocity: Velocity refers to the speed at which the data is generated, collected and analyzed. This data continuously flows through the “Internet of things”, mobile data or social media. So far so good?
- Variety: The third V is the Variety and it refers to the different sources of data generated either by humans or by machines. We can identify three types of data: Structured, Semi-structured and Unstructured.
- Structured data are often numbers or labels, stored in a structured framework of columns and rows relating to pre-set parameters. For example the star ratings we give to companies on Google reviews.
- Semi-structured data, are loosely organized into categories using meta tags. For example, Tweets that we organize by hashtags.
- Unstructured data can be text-heavy information that’s not organized in a clearly defined framework or model. For example videos and images.
- Veracity: It refers to the assurance of quality, integrity, credibility and accuracy of the data. In other words, can you trust the data that you have collected? Is this data credible enough to glean insights from? All these questions and more, can be answered when the veracity of the data is known.
- Value: The last V is the Value, which refers to how worthy the data is of positively impacting a company’s business. The Value introduces the main topic of this module, as this is where Big Data analytics come into the picture, but we will see what analytics are and how they work in the next chapter.
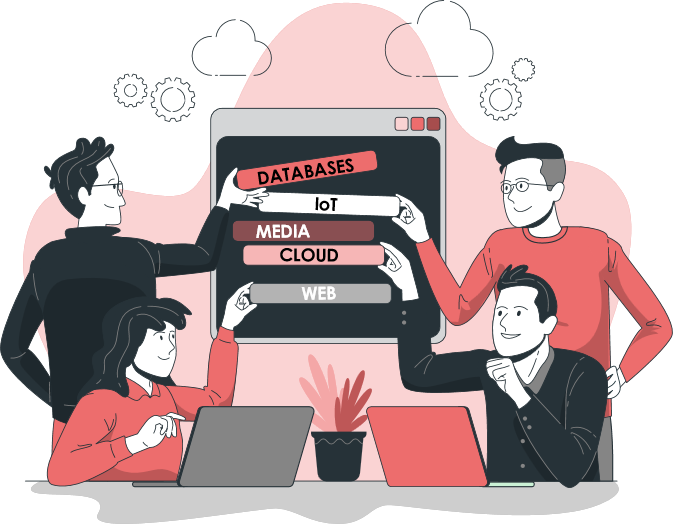
Big Data sources
Now that you know what Big Data is, it is time to learn what the sources are. The amount of data generated every day is enormous and exists in various forms. If you want to be successful with Big Data, it is important that you know how to differentiate between the various data sources available and understand how useful and relevant for your company they can be.

Edited from Source: https://storyset.com/illustration/open-source/bro
Databases
The term database sounds familiar, doesn’t it? Nowadays, companies are using a hybrid model that integrates traditional and modern databases to acquire relevant big data. Why? They simply require low investment and IT infrastructural costs. Normally, these databases are also used for several business intelligence purposes as they can provide the extraction of insights that are used to drive business profits. The most popular databases are MS Access, Oracle and SQL among others, and they can include all kind of content, as customers or articles.
Media
Media is the most popular source of Big Data, we all know platforms like Google, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Instagram. So why is media relevant? Well, it is the fastest way for businesses to get an overview of their audience, draw patterns and help their decision making as it can easily cross all physical and demographical barriers. Media, therefore, provides valuable insights on consumer preferences and changing trends.
Cloud
Cloud makes for an efficient and economical data source as big data can be stored and sourced on public or private clouds. For that reason, companies have moved from traditional data sources to cloud by shifting their data. Good examples of Cloud Computing data are Salesforce, Dropbox or IBM.
Remember what structure and unstructured data are? Cloud storage can accommodate both types of data and provides business with real-time information and on-demand insights.
The “Internet of Things”
Ever heard of Internet of Things? If not, you have the chance to learn about it in Module 4! IoT is developing fast and includes big data generated, not only from computers and smartphones, but also possibly from every device that can emit data. With IoT, data can be sourced from different devices such as video games, cameras, household appliances, and the like.
The web
Why is the web data beneficial for start-uppers? The public web constitutes Big Data that is widespread and easily accessible. Data on the Web is available to individuals and companies alike so you, start-upper, don’t have to wait to develop your own Big Data infrastructure to take advantage from it.
Analytics
What is analytics?

Source: https://storyset.com/illustration/site-stats/amico
Now that you understand what Big Data is, it’s time to know what analytics are. Literally, analytics is the “information resulting from the systematic analysis of data or statistics”[2]. Does it sound too complicated? Apparently yes, but it’s all about using the data you can collect from your website or Social Media platforms to give you insights about your business.
There are different kind of analytics that can provide a variety of insights. Since we’re just getting started, we’ll focus on the basics, and talk about the ways analytics can help you. Analytics can help you by providing data, no matter the tool you are using. But first, let’s have a look at the different types.
Different kind of analytics
It is useful to distinguish between three kinds of analytics that will tell you what has occurred, what will happen, what they will suggest you do.[3]
- Descriptive analytics reveal what has occurred. With descriptive analytics you can search and summarize historical data in order to identify patterns or meaning. How can you use descriptive analytics? Good examples are the summarising of past events such as marketing campaigns, or Social Media usage and engagement data such as Instagram likes.
- Predictive analytics suggest what will occur in the future. Since predictive analytics can tell your Start-up what could happen in the future, it will allow you to take a more proactive, data-driven approach to your business strategy and decision making. This type of analytics is based on probabilities by using a variety of techniques such as data mining or machine learning algorithms. A good example of predictive analytics will be predicting the likelihood that customers will purchase another product or leave the store.
- Prescriptive analytics will suggest what to do as they can identify optimal solutions by anticipating what, when and why something might happen. It is the most complex analytics yet the most useful to make the best possible, data-based decisions to optimise your start-up performance. A good example of prescriptive analytics is the risk assessment insurance companies do in regard to pricing for clients.
The Importance of Big Data Analytics for start uppers
Why is Big Data analytics useful for your Start-up? Basically Big Data Analytics can show you new waves of innovation and productivity growth whilst helping you to know your industry, competitors and customers. Let’s see the advantages of Big Data for your start-up in-depth.
Source: https://stories.freepik.com/illustration/startup-life/cuate
- Decision making and performance improvement: through the use of analytics, Big Data can improve your decision-making. On the other hand, as it allows you to create and store more data in digital form, you can get a detailed performance information of everything related to your start-up such as product inventories, invoices or staff schedules.
- Knowing and targeting your customers: Through customer segmentation Big Data allows more precisely tailored products or services. Furthermore, big data can help you understand better your customers behaviour through tracking their buying routine and monitoring Social Media.
- Finding innovative business models, products and services and exploring trends: Big Data can be used to improve the development of the next generation of products and services by tracking what is the customer searching or looking for, for instance with tools like Google Trends.
[1] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265775800
[2] https://www.lexico.com/definition/analytics
[3] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/276001104_All_About_Analytics

 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Polski
Polski Slovak
Slovak Español
Español Lietuvių
Lietuvių Português
Português